2. Activation Function Part - 1
Why neural network architecture uses activation functions?
An introduction to activation function and it’s importance in neural network.
Prerequisite
Before start talking about the activation function, we first need to understand neural network architecture (neuron, weight & bias) & forward propagation. If these words or concepts are unfamiliar to you then you should check out the previous article: What is Deep Learning & How Does it Work?
What is an Activation Function?
When a neural network architecture is created, a specific activation function is placed after each hidden and output layer. Now the question is What is this activation function? In plain English, the activation function determines which neuron to activate based on the input of that particular neuron. If the neuron is activated then only the value is forwarded to the next layer. So, the activation function determines which neuron’s value would go to the next layer and which neuron’s value won’t go to the next layer by activating and deactivating them. The activation function not only determines which neuron’s value will go forward but also determines the value of that neuron to pass into the next layer.
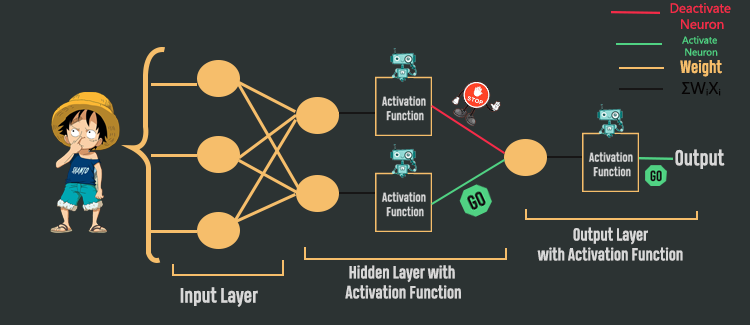
In the above picture if you look carefully then you can see the first neuron in the hidden layer goes through the activation function & after going to the activation function the neuron was deactivated, meaning its value won’t go forward. But the 2nd neuron of the hidden layer goes through the activation function and that neuron was activated, meaning its value will go to the next layer. One important thing to notice here is that activation functions are applied only after the hidden and output layer. Activation functions are not applied after the input layer.
Why use Activation Function?
There are 2 main reasons to use activation function in neural networks, those are:
- To solve a non-linear problem statement.
- Backpropagation isn’t possible without the activation function.
1. Solving non-linear problem statement
In the previous article we discussed forward propagation. In forward propagation, each neuron uses an equation to find out the output value of that particular neuron. That equation is a linear equation:
Every neuron inside the neural network uses the above equation to calculate the output of that neuron. Now the problem is the equation is a linear equation, then if all the neuron uses the same linear equation then the final output will always be a linear equation’s output. This means, if several linear equations are combined, they will eventually become a single linear equation. So, using only linear equations we can’t solve any non-linear problem.
To solve this problem activation functions are introduced inside the neural network. To solve any non-linear problem using the neural network, we simply place a non-linear activation function at the end of a layer (hidden & output layer). The output that comes from the linear equation goes inside the non-linear activation function. Now, the final output won’t be a linear equation’s output rather it’ll be a non-linear activation function’s output. And, that is how non-linearity is being introduced to a neuron’s output which will solve the non-linear problem statement.
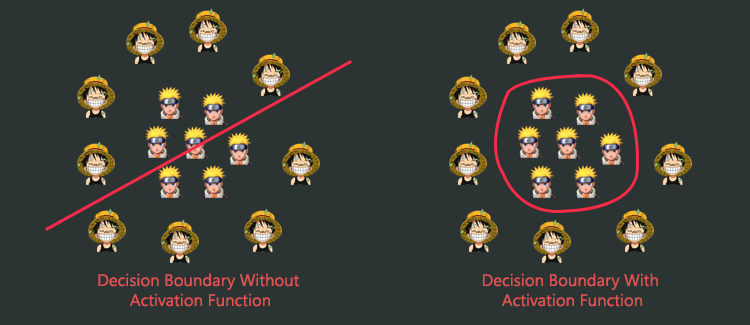
without Activation Function Vs with Activation Function
In the above picture, there are 2 classes and the decision boundary to separate these 2 classes is a non-linear problem statement. When the neural network without activation function tries to find the decision boundary to separate these 2 classes it comes up with a linear decision boundary. We can see that the linear decision boundary isn’t able to separate these classes. But when the neural network with activation function is used it finds a non-linear decision boundary to separate 2 classes. And the non-linear decision boundary can separate those classes perfectly.
2. Activation Function is Necessary for BackPropagation.
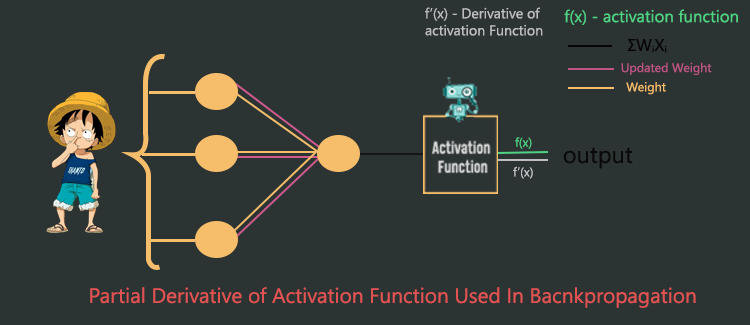
Backpropagation is one of the important steps in neural network training. Using backpropagation the neural network is able to update its weights to solve a specific problem. Now, backpropagation isn’t possible without the activation function. It’s because, when using the backpropagation algorithm to update weights the backpropagation algorithm requires finding the derivative of the activation function in every layer. If there is no activation function then there won’t be any derivative of the activation function hence the backpropagation algorithm won’t work (remember that, the activation function always has to be a differentiable function).
If you’re overwhelmed by reading derivative, differentiable functions. Please don’t worry about these terms at this moment. In the future, I’ll be writing a dedicated blog on the backpropagation algorithm. For now, just understand that without the activation function, the backpropagation algorithm won’t work.
Activation Function Part 2 (different types of activation function)
In this blog, we’ve discussed mainly what is activation function and why it is necessary for a neural network. But we haven’t discussed different types of activation functions. There are many types of activation functions such as linear activation functions and non-linear activation functions. And we have many different types of non-linear activation functions such as Relu, Leaky Relu, Sigmoid, PRelu, Softmax, etc. In the next blog Activation Function Part 2 we’ll discuss these activation functions, their pros, and their cons, and when to use them.